|
One case from the dataset and its available MRI sequences. The proposed model was trained only on DWI B1000, T2S and T2 FLAIR. 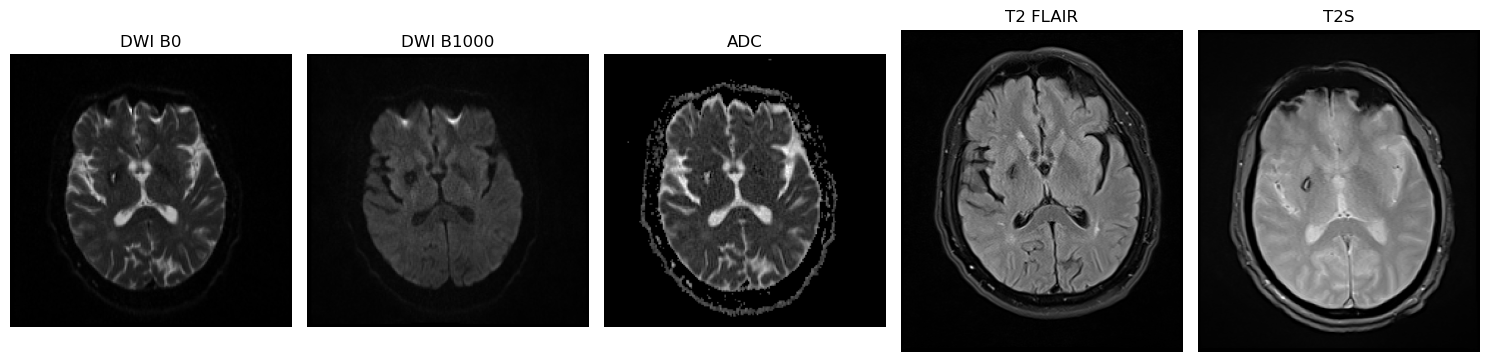
|
|
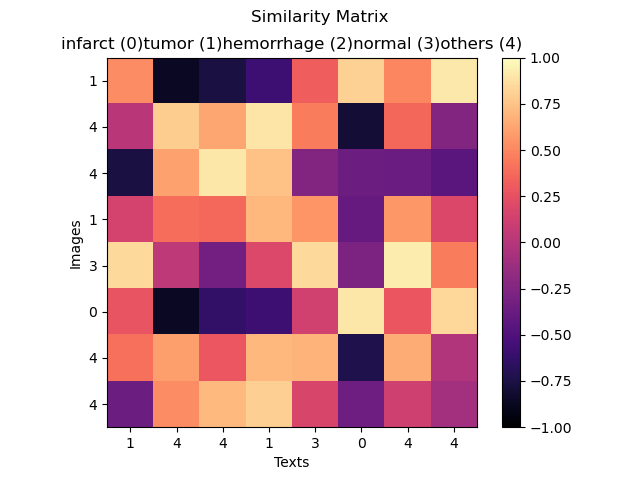
Example of a similarity matrix computed on one batch during training. The ideal matrix is the identity matrix, with values equal to one (bright) on the diagonal. However, when training on similar sample, we would also expect images with the same class to have higher similarity values. 
|
|
For each report in the test set, we compute its similarity between each other sample. We plot the similarity score for each pair-pair match only if they have the same ground truth class annotation.. 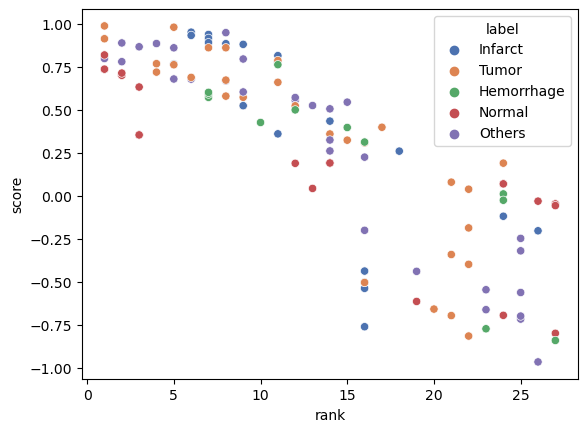
|